Unleashing the power of 3D in Draftsight Enterprise Plus
Introduction:
DraftSight has long been recognized for its precision 2D drafting capabilities. But with the evolution of design workflows, engineers and designers now need to visualize and model their ideas in three dimensions. The 3D Workspace in DraftSight Enterprise Plus brings exactly that — powerful 3D modeling tools integrated into a familiar drafting environment.
Unleashing the power of 3D in Draftsight Enterprise Plus Step-by-Step Guide:
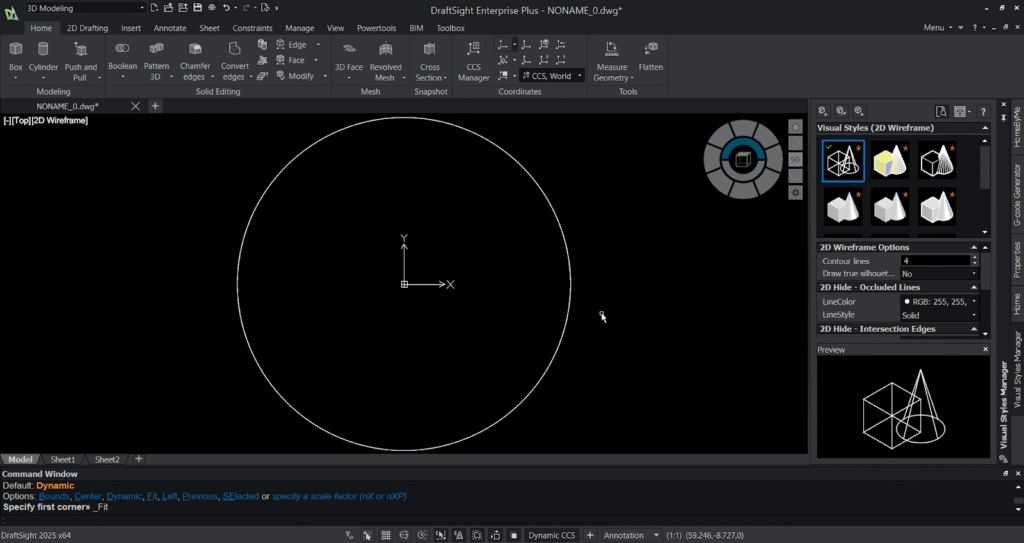
Step 1: Make a 2d sketch
- Create a circle using the “cir” command and press enter.
- Then select (0,0) as centre point and the enter 50 as radius.
- Then press enter , the circle is generated in the graphical area.
Step 2: Switch the workspace
The workspace in DraftSight provides a flexible environment that adapts to your design needs, offering predefined layouts such as 2D Drafting and 3D Modeling. Users can easily switch between these workspaces depending on their tasks or customize their own by arranging toolbars, ribbons, and palettes for maximum efficiency. Customized workspaces can be saved, transferred, and reused across systems, ensuring consistency and productivity for teams. This flexibility allows designers to maintain a clean, task-specific interface and focus more on drafting, detailing, or modeling without unnecessary distractions.
- Switch the workspace from existing to 3D Modeling workspace.
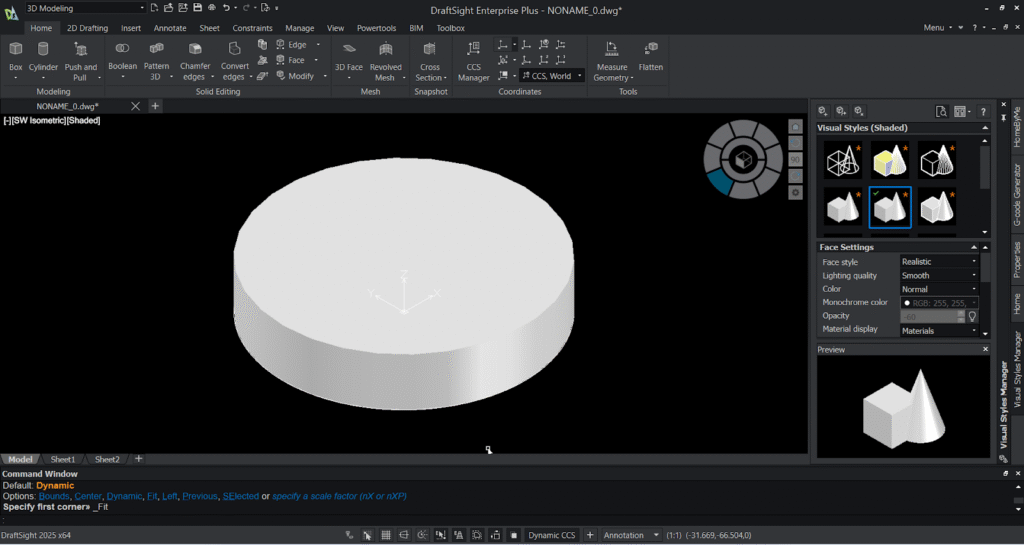
Step 3: Extrude the circle:
You can also use push and pull option to extrude your entity. The Push and Pull option in DraftSight allows users to quickly create or modify 3D geometry from 2D shapes. By selecting a face or a closed boundary, you can pull it outward to add material or push it inward to remove material, effectively extruding or cutting the solid. This intuitive tool makes 3D modeling faster and more visual, as you can dynamically adjust the height or depth of features directly in the graphics area. It’s especially useful for quickly turning 2D sketches into 3D models or refining existing designs without needing complex commands.
- Set the view to SW Isometric using the view option in the view tab or by the navigator wheel present in the graphical area.
- Then select the extrude option from the modelling ribbon in the home tab.
- Then select the circle and specify the height 20mm to be extruded.
- The extruded circle appears in the graphical area in wireframe visuals.
- Go to the visual style manager from the view tab and select the shaded with edges .
- You can notice the wireframe visual gets converted to solid visual with shaded edges in the graphical area.
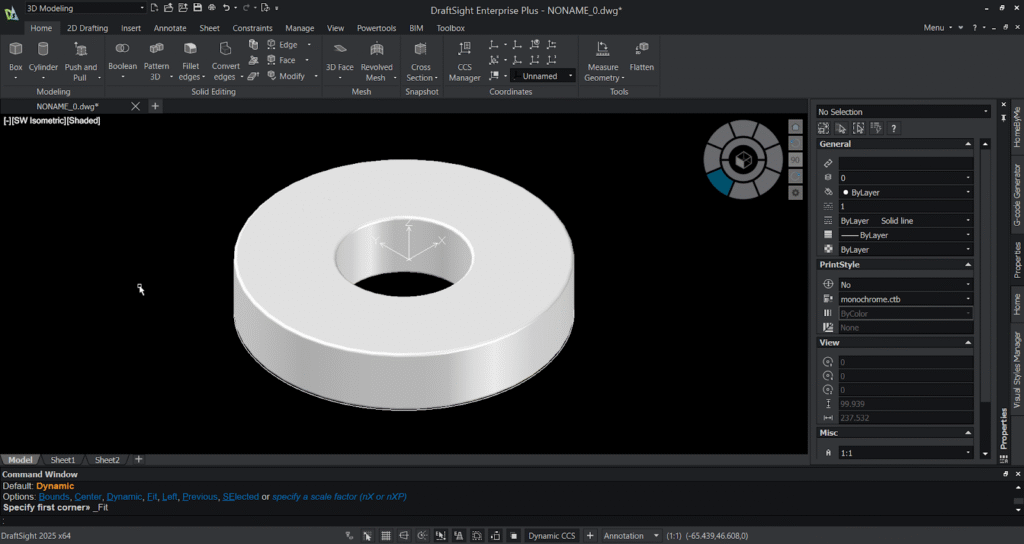
Step 4: Subtract a hole in the 3D model:
- Change the UCS by typing UCS ,select the top view through the navigator and select the view option.
- Create a cylinder in the centre of the circle.
- Specify the centre point and, specify Radius as 20mm and height as 20mm towards downwards.
- You can notice the cylinder gets created in the centre of the 3D model.
- Select the subtract option from the solid editing ribbon in the home tab . Select the 3D circle first and select the cylinder next . You can notice the hole gets created in the 3D model.
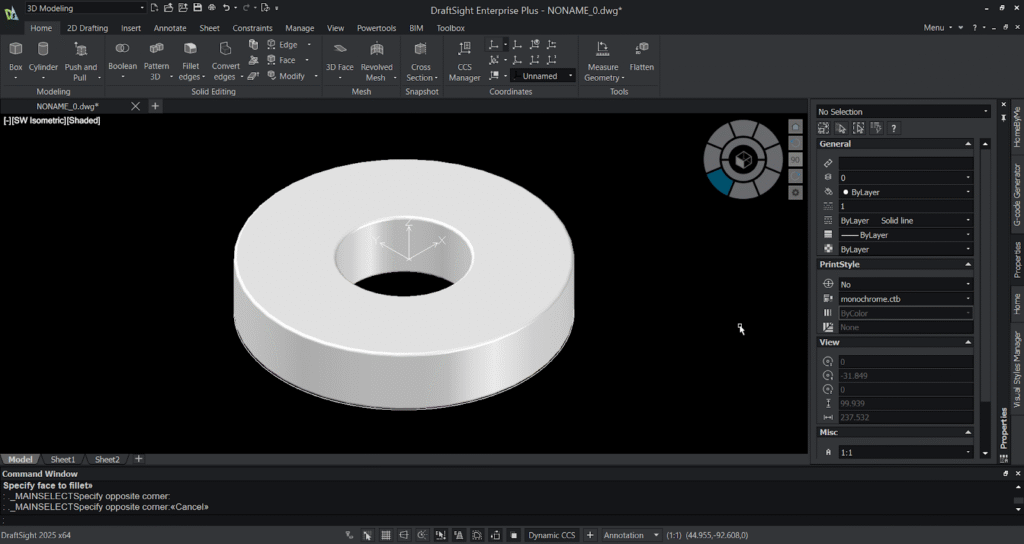
Step 5: Fillet the edges:
- Select the fillet edges or type fillet and press enter.
- Select the edges need to be filleted in the 3D model and specify the radius and then press enter.
- You’ll notice the fillet gets generated in the specified 3D model edges.
Step 6: Create holes and pattern it:
The 3D Pattern feature in DraftSight helps you quickly duplicate 3D objects in a specified arrangement, such as linear, circular, or along a path. It allows you to define the number of instances, spacing, and direction, making it easy to create repetitive features like holes, ribs, or slots. This tool saves significant modeling time by automating the duplication process instead of manually copying and positioning each object. Using 3D Pattern enhances design accuracy and consistency, especially in complex assemblies or symmetrical parts.
- Create a cylinder on the top face of the 3D model and specify its height as 20mm downwards and you’ll notice the cylinder gets created.
- Select the 3D pattern option and specify the entity(cylinder) ,enter the no .of components needed to be patterned as 4 , specify the angle as 360 degrees ,select the rotation of the component as “no” and specify the centre of axis (two points).
- Then select the subtract option and select the 3D model first and select the four patterned cylinders.
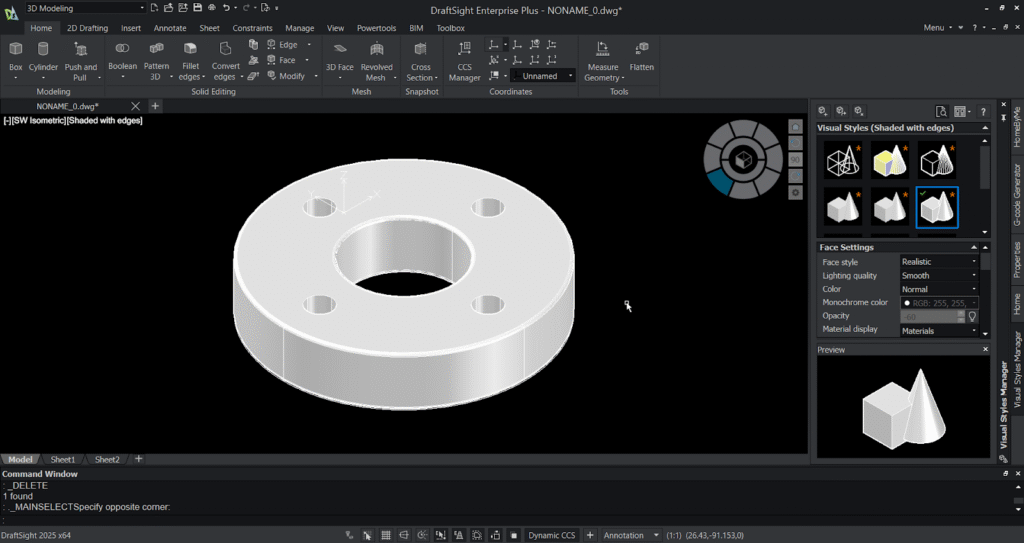
Step 7: Modify / move / rotate the solid:
- MOVE: select object, pick base point, pick destination.
- ROTATE3D (or ROTATE with axis setting): rotate around an axis by degrees .You can also rotate by just pressing “shift” +”left click” +scroll wheel” to rotate your 3D model.
- MIRROR3D: create symmetrical features.

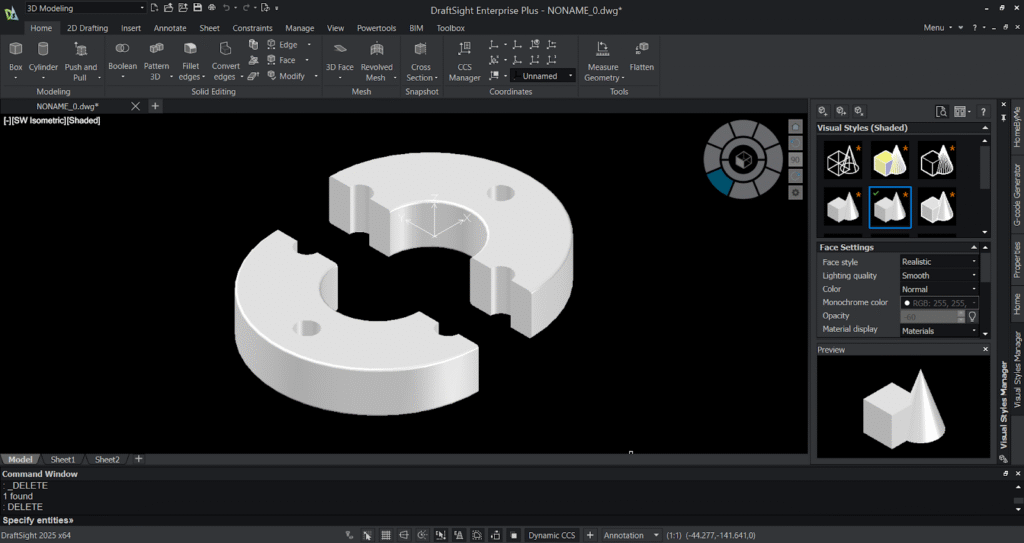
Step 8: Section or slice 3D model:
- Select the slice option from the ribbon and specify the entity.
- Select the two points of your slicing plane and select the point for placing the slicing plane.
- And press “Enter” and you’ll notice your 3D model gets sliced or sectioned.
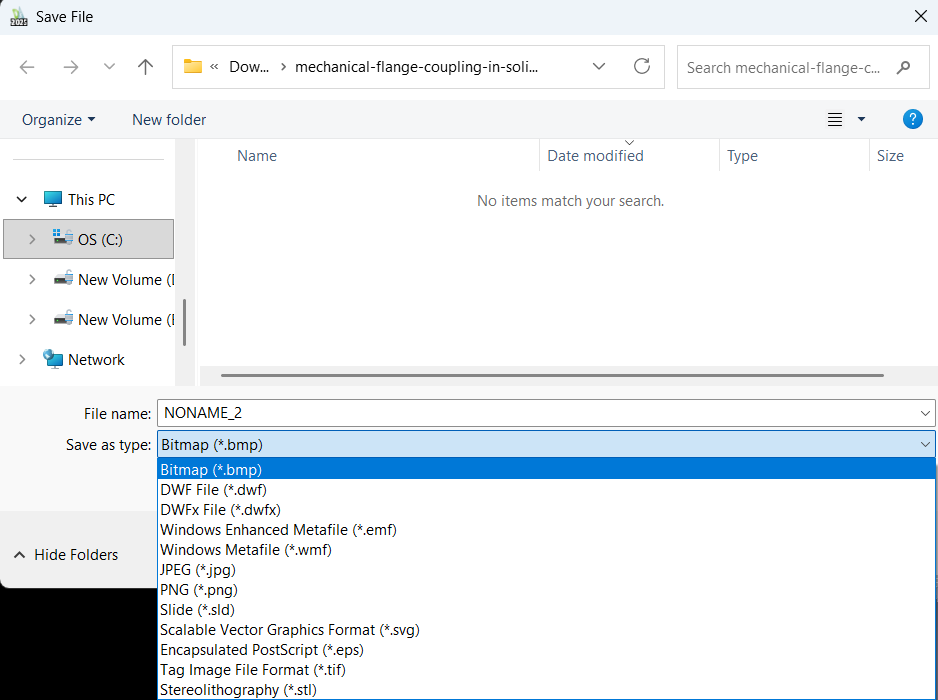
Step 9: Exporting / saving your 3D model:
The DraftSight Connector allows users to seamlessly export and manage their drawings on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform. With this integration, you can directly save your DraftSight files (.dwg or .dxf) to the cloud-based platform, ensuring secure storage and easy access from anywhere. It also enables version control, collaboration, and lifecycle management, allowing team members to review, share, and update drawings efficiently. By exporting to 3DEXPERIENCE, you bridge your DraftSight design workflow with Dassault Systèmes’ digital ecosystem, enhancing teamwork, data security, and project traceability.
- To save native: File → Save → .dwg (default).
- To export STL for 3D printing: File → Export → STL (choose mesh resolution if prompted).
- You can also export your 3D model as “SAT” file for using it in multiple CAD software.
Additional feature : Importing “Step” file :
- File → Import → select .stp or .step file (or type IMPORT and choose STEP).
- DraftSight will convert the STEP geometry to native solids/surfaces.
Conclusion:
The 3D Workspace in DraftSight converts 2D drafting workflows into a practical 3D modeling pipeline—letting you quickly create primitives, extrude 2D sketches, perform Boolean operations, and edit imported STEP models. By following the steps above you can set up your environment, model parts, clean imported geometry, inspect designs, and export for manufacturing or documentation. Start small (simple primitives and extrudes), practice the key edits (PRESSPULL, SLICE, FILLET), and you’ll gain confidence to handle assemblies and STEP imports effectively. Once comfortable, combine these workflows with DraftSight’s 2D drawing tools to produce complete, production-ready documentation from a single DWG-based environment.